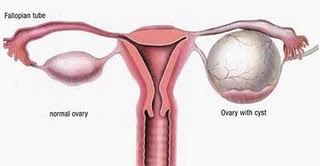
Ovarian Cysts In Conventional Medicine Perspective
Ovarian cysts affect women of all ages, especially during a woman’s childbearing years. Most ovarian cysts are functional and benign but some can become cancerous. Some ovarian cysts can cause bleeding and pain such as endometriomas/chocolate cysts and surgery is required for any cyst larger than 5 cms in diameter or if the cyst has interfered with the extruding of mature follicle. Traditional Chinese medicine defines ovarian cyst is a medical condition caused by excess- dampness (caused by blood and fluid stasis) accumulated in the abdomen and gradually coalesces into phlegm, that can manifest as that can manifest as ovarian cysts or various kinds, including chocolate cysts. In conventional medicine, ovarian cysts is defined as a cI. Types of ovarian cysts
1. Follicular cyst:
Follicular cyst normally forms at the time of ovulation as a result of mature follicle has become involution or when ovulation does not occur. That means there is a follicle which doesn’t rupture or release its egg but instead grows in the ovaries and becomes a cyst. During every month of menstrual cycle when ovulation occurs,the follicular cyst may rupture, causing severe pain on the side of the ovary.
2. Corpus luteum cyst:
After an egg has been released from a follicle, the follicle becomes a corpus luteum, if no pregnancy occurs, it normally breaks down and disappears. Unfortunately, in some women, a corpus luteum may persist on the ovary filled with fluid or blood.
3. Hemorrhagic cyst:
Hemorrhagic syst is defined as a condition of bleeding within the cyst, causing abdominal pain in the side of ovary where the cyst locates.
4. Dermoid cyst:
It is a type of benign large tumor can grow to 6 inches in diameter which affects mostly in the population of younger women.
5) Endometriomas or chocolate cysts:
Endometriomas – Chocolate Cysts are definition as a health condition of endometrial cells forming in the outside of the ovaries, leading to endometriosis on the surface of the ovaries. They also react to hormone stimulation during the menstrual cycle, by building up tissue, breaks it and eliminates it through menstrual period that causes blood spilling over the abdominal cavity, causing menstrual cramps and pain. Since chocolate cysts – endometriomas are filled with a thick chocolate-type material, they are called chocolate cysts.
6) Polycystic-appearing ovary:
Polycystic-appearing ovary is defined as a condition of enlarged size with small cysts present around the outside of the ovary. This condition is usually find in women with or without endocrine disorders.
7. Polycystic ovarian syndrome
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome is defined as endocrinologic diseases caused by undeveloped follicles clumping on the ovaries that interferes with the function of the normal ovaries as resulting of enlarged ovaries, leading to hormone imbalance( excessive androgen), resulting in male pattern hair development, acne,irregular period or absence of period, weight gain and effecting fertility. It effects over 5% of women population or 1 in 20 women.
7) Cystadenoma:
A cystadenoma is defined as a condition of development of benign cyst which can grows to 12 inches in diameter and is filled with a mucous-type fluid material which develop from the tissues of ovary.ollection of fluid, surrounded by a very thin wall, within an ovary.
II. Causes of Ovarian Cysts
1. History of previous ovarian cysts
Ovarian cysts have a tendency to grow back, after surgery and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine due to stress, improper diet and other extenal or internal pathogenic factors, we will clarify more detail in the next article – ovarian cysts in traditional Chinese medicine.
2. Irregular menstrual cycles
Most women with ovarian cysts also associate with irregular menstrual cycle a, leading to ovulation disorder that increases the risk of the development of ovarian cysts.
3. Increased upper body stout distribution
Suddenly onset of body stout increasing may be caused by insulin resistance, leading to developing of ovarian cysts.
4. Early menstruation
Since ovarian cysts tends to occur in younger women, early menstruation in younger age can increase the risk of this type of abnormal cell growth.
5. Infertility
If the cysts are grown large enough or become cancerous, they may block the fallopian tube, thus interfering with normal process of egg extruding from the ovary to the fallopian tube. It may also interfere with the ovulation phrase of menstrual cycle.
6. Hypothyroidism or hormonal imbalance
Hypothyroidiwm or hormone imbalance can cause irregular menstrual cycle, leading to development of follicle with in-ovulation or no ovulation occurs.
7. Tamoxifen therapy for breast cancer
researcher found that women who use tamoxifen to treat cancer are higher risk to develop ovarian cysts.
8. Painful sex
If the cysts are grow large enough, they may cause painful sex, due to the contraction of abdominal muscles.
9. Etc
III. Symptoms of ovarian cysts
1. Lower abdominal pain
2. Irregular menstrual periods
3. Pressure and pain in the abdomen
4. Long-term pelvic pain during menstrual period
5. Pelvic pain after strenuous exercise or sexual intercourse
6. Pain or pressure with urination or bowel movements
7. Nausea and vomiting
8. Vaginal pain or spots of blood from vagina
9. Infertility
10. Painful sex
11. Breast tenderness
12. dizziness
13. Fatigue and tiredness
14. Etc.
IV. Diagnosis
1. Endo-vaginal ultrasound:
If you doctor suspects that you may have develop ovarian cysts, he or she may order ultra sound Ultrasound to exam your pelvic organs. A cyst can be diagnosed based on its appearance on the ultrasound.
2. CT scanning
If your uttrasound image has found ovarian cysts, you doctor may want to confirm it by ordering the CT scan.
3. Laparoscopic surgery:
With a woman abdomen is filled with a gas, your doctor makes small incision and a laparoscope passes into your abdomen. By examining your abdomen through the laparoscope, he or she can view the cysts and removes them or take a biopsy.
4. Serum CA-125 assay
finally if the ovarian cysts are identified, a blood test called CA-125 to checks for a substance called CA-125, which can tell your doctor if the ovarian cysts have become cancerous.The levels elevation of CA- 125 is associated with high risk of cancerous ovarian cysts.
5. Etc.
V. Types of Treatment
Since most of ovarian cysts are harmless they do not pose a threat to most women’s health. Most doctors suggest to use ultrasonic observation or endovaginal ultrasound to monitor the growth of the cyst frequently, unless there is necessary then surgery may be required to remove them such as interfering with infertility.
If fertility is not a concern then
A. Oral Contraceptives
I. The excellent
a) Control unwanted pregnancy
The pill beside reducing the period pain, it also helps to protect woman against any unwanted pregnancy, because it stop or reduce period, making a continual pregancy like state resulting of not letting sperm near you.
b) Control menstrual cramps
It helps to inhibit the over production of prostaglandins which cause the muscles spam contraction of ovarian muscles resulting of less period pain and period flow.
c) Reducing the rate of reproductive organ diseases
Study shows that intake of oral contraceptive combination pill helps reduce the rate of ovarian and endometrial cancer, benign breast disease, benign ovarian cysts, pelvic inflammatory disease, because of stopping or reducing of period blood flow.
d) Shinking ovarian cysts
Ovarian cysts no longer active, because there are no substance to activate the menstrual cycle because of pregnancy like state that shrinks the endometriosis.
e) Anemia
Since anemia is a disease of iron deficiency, intake of the pill stops or reduces the period blood, there are less iron needed to be produced by the liver or other organs.
2. The terrible
a) Growth of fibroids
Fibroid starts from a single cell that grows abnormally. Fibroid occurs mostly in women after puberty puberty and shrink after menopause. Growth of fibroid is caused high level of estrogen and progesterone. The intake of the pill increase the level of both hormones resulting in increase the risk of growth of fibroid.
b) Recurrent of menstrual symptoms
Some women stop taking the pill may see all the menstrual symptoms coming back.
c) Blood clots
Intake of estrogen through the pill cause the blood getting thicker resulting in blood clots in the small vessels in the leg and the lung.
d) Stroke and heart diseases
Study shows that women who have higher natural estrogen levels may have a higher risk of stroke and heart diseases caused by estrogen in the pill that blocks that hormonal action in some parts of the body, while increasing its effects in the heart and others
e) Hormonal imbalance
The pill may influence the imbalance hormones of estrogen and progestone. Normally, It require six months for the body to adjust to the intake of oral contraceptive pill.
f) Depression and mood swing
The intake of the pill at the beginning may cause abnormal fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone elevate both physical and psychological stress, eventually resulting in both depression and mood swing. If depression and mood swing continue over six months period, it is for your own excellent to talk to your doctor for other pills.
g) Infertility
Prolong used of oral contraceptive combination pill may cause loss of period in some women. Some women may take months or year to get their period back. resulting of infertility.
3. The hideous
a) Bleeding and spotting
Bleeding and spotting is normal for the first six months for women starting any oral contraceptive combination pill because our body needs time to adjust to the new medication.
b) Lost interest in sex
Women who take the contraceptive pill are in danger of permanently lost their interest in sex because the oral contraceptive pill inhibits testosterone, the hormone that drives sexual desire even aftyer if they stop the pill.
c) Chloasma or melasma
It caused by hormonal changes, as in pregnancy and intake of estrogen in the oral contraceptive pill.
d) Nutritional deficiency
Oral contraceptive pill causes vitamin and mineral imbalances or deficiencies. It depletes magnesium for healthy heart, coenzyme Q10 for healthy heart muscles, folic acid for preventing cervical abnormalities, vitamin B6, B2, B3, zinc, etc.
If fertility is a concern, please read the below carefully
B. Oophorectomy
If both ovaries are removed, the you can not get pregnant, if only one side of ovary is removed, then it will not affecting to your future pregnancy. therefore the procedure is considered as a last-resort option in cases of ovarian cysts and ovarian cancer.
I. Definition
Also known as ovariotomy, oophorectomy is a medical procedure to have one ovary removed, if ovarian cysts have become cancerous. After oophorectomy, the woman will continue to have menstrual cycle and can not become pregnant, if both ovaries are removed.
II. How it work
General anesthesia is needed and the operation is done in the hospital.
a) Normally, Unilateral oophorectomy is done with a laparoscopic procedure as we mentioned in previous article. Laparoscope is a thin tube containing a tiny lens and light that inserts through a small incision in the navel with a camera on the other end that allows your doctor to see the abdominal cavity on a video monitor. After the ovary is detached, it is removed though a small incision at the top of the vagina.
b) Vertical incisions
Vertical incisions give the doctor better view of of the abdominal cavity but it will leave some notable scar. If cancer is detected, a vertical abdominal incision is needed. After the incision the ovary is removed
c) Horizontal incision
If the ovary is removed by horizontal incisions it will leave a less notable scar.
III. Risk and side effects
a) Heavy blood loss caused by medical instrument used during surgery.
b) Heaving bleeding during or after operation
c) Infection of the incision area, may be caused by bacteria or medical instruments.
d) Needed to stay to hospital for 2 – 5 days
e) Time to recover is longer. It may take 3- 6 weeks to return to normal activity.
IV. Other medical term
a) Bilateral oophorectomy
Both ovaries are removed
b) Unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy
Remove one Fallopian tube and one ovary in the same side
c) Bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy
Remove both Fallopian tubes and ovaries.
If fertility is a concern
3. Cystectomy
This operation may be helpful if the ovarian systs have not become cancerous and fertility is a concern, because a cystectomy is effective in treating non cancerous ovarian cysts by removing only part or all of the bladder, gallbladder or any cyst in the pelvic region, including ovarian cysts but not interfering with women’s future ability to have children.
I hope this information are helpful, if you need more information of women health, please visit
http://medicaladvisorjournals.blogspot.com
or Infertility And PCOs in Conventional Medicine, TCM & Weight Loss perspective
http://steady-health-1.blogspot.com/
or Ovarian Cysts in Traditional Chinese perspective
http://ovairancysts1.blogspot.com/
Article Source: http://www.articlesbase.com/womens-health-articles/ovarian-cysts-in-conventional-medicine-perspective-1760929.html